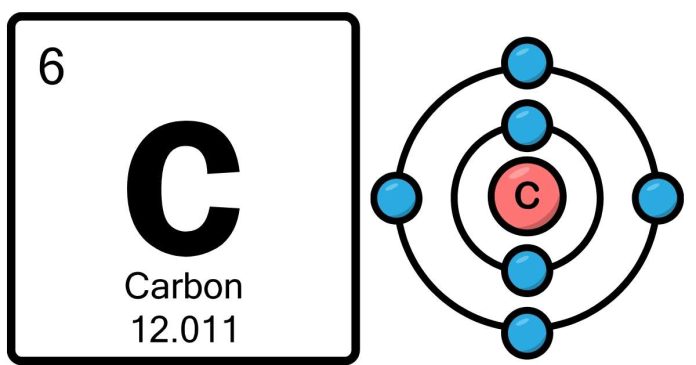
Atomic Number and Atomic Structure:
- Atomic Number: Carbon has an atomic number of 6, meaning it has 6 protons in its nucleus. The atomic number uniquely identifies an element on the periodic table.
- Electron Configuration: A neutral carbon atom also has 6 electrons, which are arranged in electron shells around the nucleus. The distribution of these electrons is crucial for understanding how carbon interacts with other elements.
- The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons, so it contains 2 electrons.
- The second shell can hold up to 8 electrons, so it holds 4 electrons in carbon.
This gives carbon an electron configuration of 1s² 2s² 2p², where:
- 1s²: 2 electrons in the first energy level (closest to the nucleus).
- 2s² 2p²: 4 electrons in the second energy level, spread across the s and p orbitals.
Chemical Properties and Bonding:
- Valence Electrons: The key to carbon’s chemical properties lies in its 4 valence electrons (those in the outermost shell, the second shell). These 4 electrons are available to form bonds with other atoms.
- Covalent Bonding: Carbon’s ability to form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms (such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, or other carbon atoms) is essential to the structure of organic molecules. For instance:
- In methane (CH₄), carbon bonds with 4 hydrogen atoms, using its 4 valence electrons to share one electron with each hydrogen atom.
- In carbon dioxide (CO₂), carbon forms double bonds with two oxygen atoms.
This bonding capability is a big reason why carbon is central to the chemistry of life—its flexibility allows it to form a wide variety of complex molecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates.
Role in Organic Chemistry and Life:
- Organic Chemistry: Carbon is the backbone of organic chemistry, which is the study of carbon-containing compounds. It can form long chains, rings, and complex structures by bonding with other carbon atoms, which is why it’s found in so many biological molecules.
- Life’s Building Blocks: Carbon’s ability to form stable, versatile bonds allows it to be the key element in molecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins, which are essential to life. The diversity of organic compounds made possible by carbon is unparalleled in nature.
- Allotropes: Carbon exists in several different allotropes, which are different forms of the same element that have different structural arrangements. Some common forms include:
- Diamond: Carbon atoms arranged in a very rigid lattice, making it one of the hardest substances known.
- Graphite: Carbon atoms arranged in layers that can slide over each other, making it useful as a lubricant and in pencils.
- Fullerenes (Buckyballs) and Nanotubes: Spherical or tubular forms of carbon, which are of great interest in materials science and nanotechnology.
Importance of Carbon in Nature:
- Carbon Cycle: Carbon is a crucial part of the carbon cycle on Earth, where it is exchanged between the atmosphere, oceans, and living organisms. Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) during photosynthesis, which is then passed on through the food chain, and animals respire CO₂ back into the atmosphere.
- Global Warming: Because carbon dioxide (CO₂) is a greenhouse gas, the balance of carbon in the atmosphere plays a role in regulating Earth’s temperature. Excessive carbon emissions, mainly from burning fossil fuels, have contributed to global warming.
Summary:
The atomic number 6 signifies that carbon has 6 protons and 6 electrons, which makes it a versatile element in forming bonds, especially through its 4 valence electrons. This ability to form stable covalent bonds with many elements is fundamental to the existence of life and the complexity of organic compounds. From diamonds to DNA, carbon’s unique properties enable a vast array of structures and functions, both in the natural world and in synthetic materials.