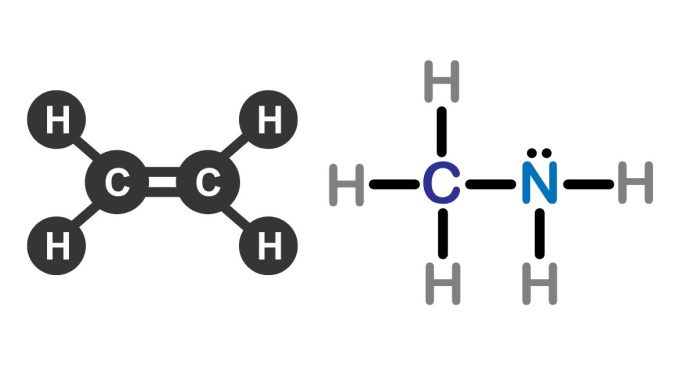
The Lewis structure of ethylamine (C₂H₅N) illustrates the arrangement of atoms and valence electrons within the molecule. Ethylamine consists of two carbon atoms (C), five hydrogen atoms (H), and one nitrogen atom (N), with the following connectivity:
- Carbon Backbone: The two carbon atoms are single-bonded, forming a chain.
- Hydrogen Atoms: Four hydrogens are bonded to the first carbon (CH₃ group), and one hydrogen is bonded to the second carbon (CH₂ group).
- Nitrogen Atom: The nitrogen atom is single-bonded to the second carbon and has a lone pair of electrons. It is also bonded to two hydrogen atoms, completing its valency.
Electron Configuration
- Each single bond represents a pair of shared electrons.
- The nitrogen atom has one lone pair, which is not involved in bonding but contributes to the molecule’s shape and properties.
Geometry
The molecule has a trigonal pyramidal geometry around the nitrogen due to the lone pair, and the overall structure is linear along the carbon chain.
Ethylamine is a primary amine, and its Lewis structure highlights its functional group (-NH₂), which is critical to its chemical reactivity and interactions.