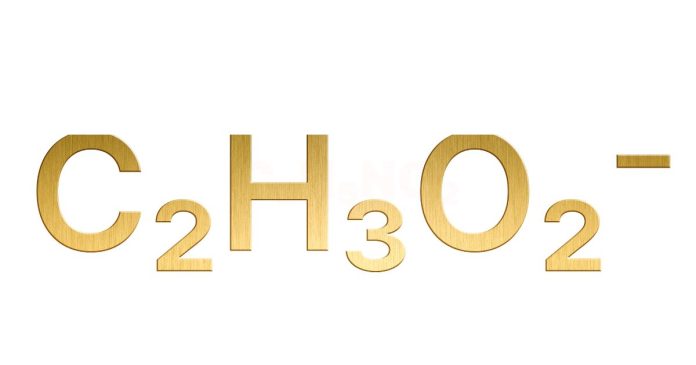The empirical formula of a compound represents the simplest whole-number ratio of its constituent elements. Acetic acid has the molecular formula HC₂H₃O₂, which means it contains 2 carbon atoms, 4 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. To determine the empirical formula, divide the subscripts of each element by their greatest common divisor (GCD), which is 2. Simplifying, the ratio becomes C:1, H:2, O:1, resulting in the empirical formula CH₂O. This represents the simplest proportion of elements in acetic acid while retaining its chemical identity. Empirical formulas are important for understanding the basic composition of compounds.
What is The Empirical Formula of Acetic Acid, HC₂H₃O₂?
RELATED ARTICLES
0 Comments
Oldest