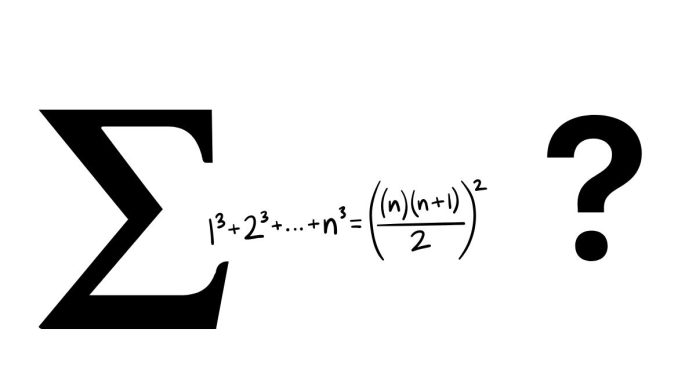The Residual Sum of Squares (RSS) is a measure used in statistics to show how much of the variation in data is not explained by a model. It tells us how far the actual data points are from the predictions made by the model.
Key Points:
What It Measures: RSS measures the total error between the actual observed values and the predicted values. The smaller the RSS, the better the model fits the data.
How It Works:
For each data point, calculate the difference between the observed value and the value predicted by the model.
Square these differences to turn all values positive.
Add up all the squared differences to get the RSS.
Why It’s Important:
It helps evaluate how well a model captures the patterns in the data.
A lower RSS means the model’s predictions are closer to the actual data points.
It can be used to compare models and choose the one that fits the data best.
In short, RSS is a way to measure the error in a model’s predictions by looking at how far off those predictions are from the actual data.