Understanding the area of the base of a rectangular prism is key to solving many geometry problems, especially when calculating volume or understanding its structure. Let’s break it down!
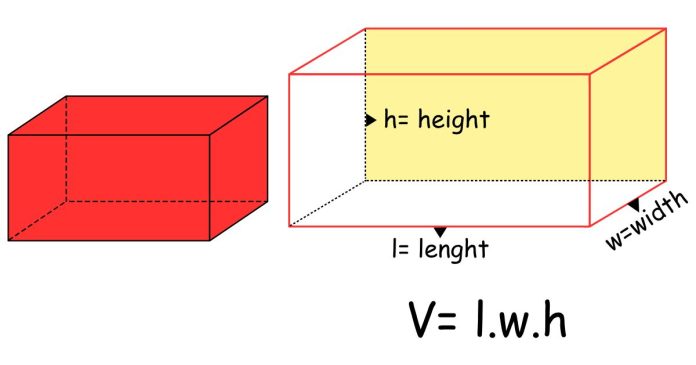
A rectangular prism is a three-dimensional shape with six rectangular faces, where opposite faces are equal in size. The base of the prism is any one of these rectangular faces, typically referred to as the “bottom” or “top,” depending on orientation.
How to Calculate the Area of the Base
The area of the base of a rectangular prism is determined by finding the area of one of its rectangular faces. You can calculate it using the following formula:
Area of the Base=Length×Width
Here’s what the terms mean:
- Length: The longer side of the rectangular base.
- Width: The shorter side of the rectangular base.
Example Calculation
Imagine a rectangular prism where the base has:
- Length = 8 cm
- Width = 5 cm
Using the formula:
Area of the Base=8 cm×5 cm=40 cm2
So, the area of the base is 40 square centimeters.
Why is the Base Area Important?
The base area is a fundamental measurement used to calculate the volume of the rectangular prism. Once you have the base area, you can find the volume by multiplying it by the prism’s height:
Volume=Base Area×Height
In summary, the area of the base of a rectangular prism is simply the product of its length and width. It’s an essential concept that forms the foundation for understanding the geometry and volume of three-dimensional shapes.