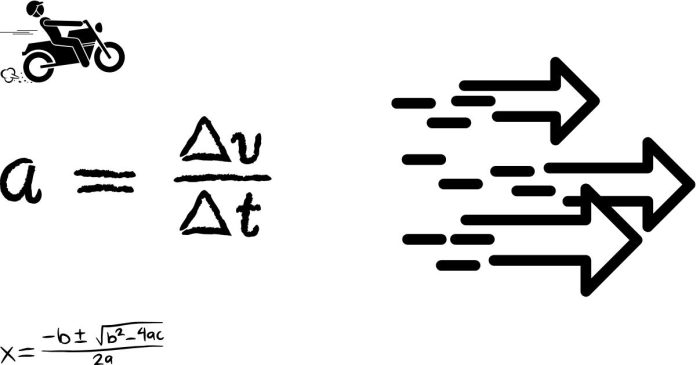Tangential Acceleration refers to the rate at which an object’s speed changes along a curved path. It acts along the direction of motion and is responsible for increasing or decreasing the speed of an object in circular motion.
For example, if a car is moving along a curved road and its speed increases, the change in speed over time is due to tangential acceleration. It depends on how quickly the object’s rotational speed is changing and the size of the circular path.
In simple terms, tangential acceleration is the part of acceleration that changes the object’s speed while moving in a circular path.