A MAC address (Media Access Control address) is a unique identifier assigned to the network interface card (NIC) of a device for use in network communications. It is used in local networks to ensure that data is sent to the correct device.
Key Points About MAC Address:
- Format:
- A MAC address is typically represented as a 12-digit hexadecimal number, often displayed in pairs separated by colons or hyphens.
- Example:
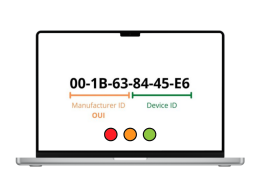
00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E
- Structure:
- The MAC address is 48 bits long (6 bytes).
- The first 3 bytes (24 bits) are assigned to the manufacturer of the device (known as the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI)).
- The last 3 bytes (24 bits) are assigned to the device itself, providing a unique identifier for each piece of hardware.
- Function:
- The primary role of a MAC address is to ensure that devices on a local network can identify each other and communicate with each other.
- It operates at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, handling communication between devices on the same local network.
- Static vs Dynamic:
- Static (Burned-in): The MAC address is typically burned into the device’s hardware and cannot be changed. This ensures that every network interface card has a globally unique MAC address.
- Dynamic: Some devices (especially in virtualized environments or network emulation) may have the ability to change or randomize their MAC addresses.
- Usage:
- In Ethernet Networks: Devices use MAC addresses to identify each other and transfer data over a network. When a device sends a data packet, the destination device’s MAC address is used to route the packet.
- Wi-Fi Networks: MAC addresses are also used in Wi-Fi to connect to routers and other devices on wireless networks.
- Difference from IP Address:
- While IP addresses are used to identify devices on a global scale (across the internet), MAC addresses are used for local network communication.
- IP addresses can change depending on the network or location, while MAC addresses are permanent for each device (unless altered manually in some cases).
- Finding the MAC Address:
- On Windows: Open Command Prompt and type
ipconfig /all. Look for the “Physical Address” field under your network adapter. - On MacOS: Go to System Preferences > Network, select your active network connection, and click on Advanced. The MAC address will be displayed there.
- On Linux: Use the command
ifconfigorip link showto find the MAC address.
- On Windows: Open Command Prompt and type
Example Use Cases:
- Network Security: Network administrators can use MAC address filtering to allow or deny access to a network based on the MAC addresses of the devices trying to connect.
- Device Identification: In a local network, the MAC address helps identify and track devices, even if they change their IP address.
- Ethernet Frame Delivery: MAC addresses ensure that data frames are delivered to the correct network interface on a local area network (LAN).
Conclusion:
A MAC address is a hardware address that uniquely identifies devices within a local network, ensuring proper communication between them. It is an essential part of network protocols and is different from the IP address used for routing packets over the internet.