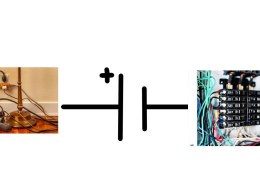An electric circuit is a closed loop or pathway that allows electric current to flow. It consists of various components that are connected in such a way that current can travel through the circuit. Electric circuits are essential in devices like lights, computers, and phones.
Basic Components of an Electric Circuit:
- Power Source (Battery/Cell): Provides the voltage (or electric potential difference) to drive the current around the circuit.
- Conductors (Wires): These allow the flow of electric current. Usually made of copper or aluminum.
- Load (Resistor, Bulb, Motor, etc.): This consumes electric power and converts it into other forms of energy (e.g., light, heat, motion).
- Switch: A component that can open or close the circuit, controlling the flow of current.
- Ground: A reference point in the circuit, typically used to complete the circuit.
Common Symbols:
- Battery/Power Source: A pair of short and long lines (longer line is positive)
- Resistor: A zig-zag line
- Wire: A straight line
- Switch: A break in the wire with a gap
- Lamp (Bulb): A circle with an “X” inside
- Ground: A set of horizontal lines stacked one above the other
Electric Circuit Formulae:
- Ohm’s Law: V=IRV = IR where:
- VV = Voltage (Volts)
- II = Current (Amps)
- RR = Resistance (Ohms)
- Power: P=IVP = IV or P=I2RP = I^2 R where:
- PP = Power (Watts)
Types of Electric Circuits:
- Series Circuit: Components are connected end to end in a single path. The current is the same through all components, but the voltage divides across them.
Example: Christmas lights (if one goes out, all go out).
- Parallel Circuit: Components are connected in multiple paths. The voltage across each component is the same, but the current splits among the different branches.
Example: Household electrical wiring (each appliance has its own path).
Example of a Simple Electric Circuit:
- A battery connected to a resistor (or light bulb) through conducting wires, with a switch to control the current flow.
In practice, electric circuits are everywhere, from the wiring in your house to the complex circuits in electronics.