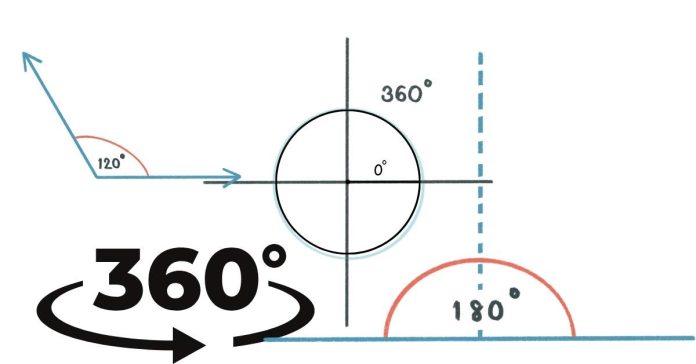
A zero-degree angle is an angle that measures exactly 0 degrees. It occurs when two rays or line segments overlap perfectly, pointing in the same direction. In this case:
The angle between them is effectively non-existent.
It appears as a single straight line because there is no separation between the rays.
Example:
If you rotate one ray to align with another without any gap, the resulting angle is 0°.
In geometric terms, a zero-degree angle is the smallest possible angle and represents no rotation.