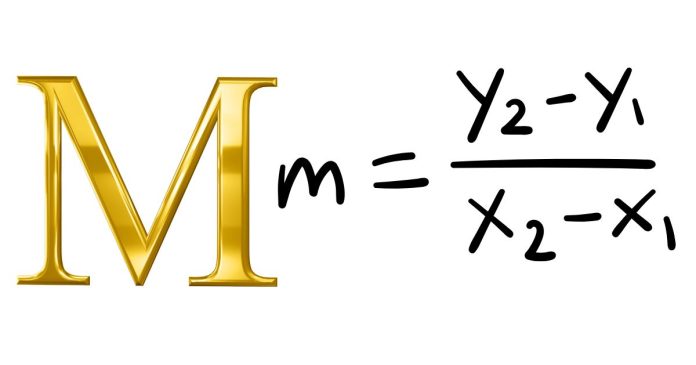In algebra, the letter M can represent a variable, just like any other letter such as x, y, or z. The value of M depends on the context of the equation or expression in which it is used. It’s important to remember that, unless specified, M doesn’t have a fixed value — it can represent any number or quantity.
Common Uses of M in Algebra
- M as a Variable:
In many algebraic expressions, M is simply a placeholder for an unknown value. For example, in the equation M + 5 = 10, M represents the unknown number that, when added to 5, equals 10. In this case, you can solve for M by subtracting 5 from both sides:
M = 10 – 5
- M as the Slope in Linear Equations:
In the slope-intercept form of a linear equation, y = mx + b, the M often represents the slope of the line. The slope indicates how steep the line is and is calculated as the change in y (vertical) over the change in x (horizontal). So, in this context, M is a constant that determines the steepness and direction of the line.
- M as a Coefficient
M can also appear as a coefficient, which is a number multiplying a variable. For example, in the expression M * x = 20, M is the coefficient of x, and solving for x would give you the value of x in terms of M.
In algebra, M is a flexible symbol used to represent an unknown value, the slope of a line, or a coefficient in an equation, among other things. The exact meaning of M depends on the specific algebraic context in which it is used. Understanding its role helps you interpret and solve algebraic problems more effectively.