What Are the Functions of Lipids?
Lipids, often known as fats and oils, are essential biomolecules that play a wide variety of roles in our bodies and in nature. From providing energy to forming cell membranes, their importance cannot be overstated. Here’s a closer look at the key functions of lipids:
1. Energy Storage
Lipids are a powerhouse of energy. They store significantly more energy per gram than carbohydrates or proteins. Triglycerides, a type of lipid, act as long-term energy reserves in animals and plants. When the body needs energy, it breaks down these stored fats to fuel physical activity and metabolic processes.
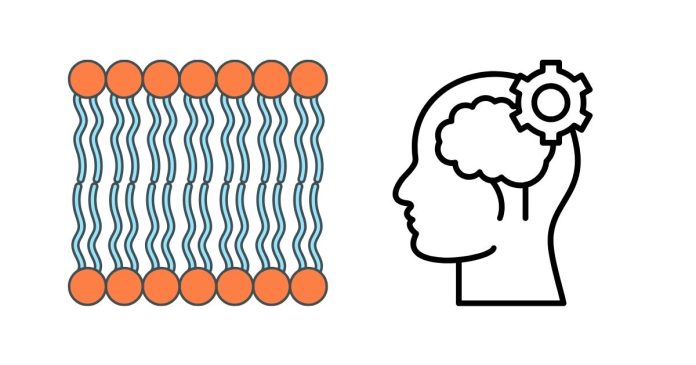
2. Building Cell Membranes
One of the most critical roles of lipids is in the formation of cell membranes. Phospholipids and cholesterol are key components of the lipid bilayer, which provides structure to the cell and regulates the movement of substances in and out of it. Without lipids, cells wouldn’t have the protective barriers they need to function.
3. Insulation and Protection
Lipids serve as natural insulators, helping organisms maintain a stable body temperature. They also cushion and protect vital organs from physical damage. This protective layer of fat ensures that organs remain safe in the face of sudden impacts or extreme temperature changes.
4. Acting as Signaling Molecules
Certain lipids, like steroids and eicosanoids, act as chemical messengers in the body. Steroid hormones such as estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol are derived from cholesterol, a lipid. These molecules regulate a wide range of processes, from metabolism to immune responses and reproductive functions.
5. Aiding in Vitamin Absorption
Fat-soluble vitamins—A, D, E, and K—rely on lipids for absorption. Without dietary fats, the body would struggle to take in these essential nutrients, which are crucial for vision, bone health, antioxidant protection, and blood clotting.
6. Waterproofing and Protection in Nature
In plants and animals, certain lipids provide a protective, waterproof barrier. For example, waxes on plant leaves prevent water loss, and the oily secretion on animal fur or feathers helps repel water, ensuring they stay warm and dry.
7. Providing Flavor and Texture in Food
In addition to their biological functions, lipids enhance the flavor, texture, and satiety of foods. They make meals more enjoyable and satisfying by carrying flavors and contributing to the creamy or crispy textures we love.
Final Thoughts
Lipids are far more than just “fats.” They’re vital for energy storage, cellular structure, insulation, communication, and nutrient absorption. Whether you’re studying biology or simply trying to understand the role of fats in your diet, appreciating the diverse functions of lipids helps us see why they are indispensable to life.