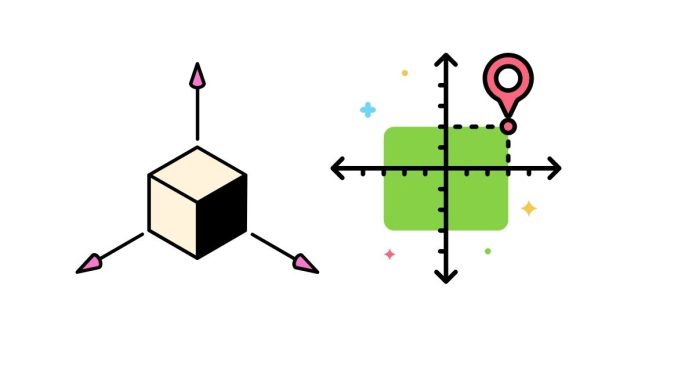
Absolute coordinates are a method of specifying a point’s exact location in a coordinate system relative to a fixed origin. The coordinates are defined as distances along the axes of the system. In 2D space, this typically involves and values, while in 3D space, , , and values are used.
Key Features of Absolute Coordinates:
1. Fixed Origin: The position is determined relative to the origin point (0, 0) in 2D or (0, 0, 0) in 3D.
2. Precise Positioning: The values directly represent the exact position without reference to other points.
3. Independent of Context: The coordinates are static and do not depend on the current location or orientation of any object.
Examples:
1. 2D Example:
The point is 5 units to the right and 3 units up from the origin.
2. 3D Example:
The point is 4 units along the -axis, 2 units along the -axis, and 7 units along the -axis.
Applications:
Computer-aided design (CAD)
Mapping and geographic information systems (GIS)
Robotics and navigation systems
Graphics and game development
In contrast, relative coordinates describe a location relative to another reference point.