The Celsius and Kelvin scales are two common temperature scales used in science and everyday life. While they are often used interchangeably in many contexts, they have distinct differences in terms of their reference points and zero points. One question that frequently arises is: Is one Celsius degree larger than a Kelvin? Let’s break it down to better understand the relationship between the two scales.
What Are Celsius and Kelvin?
Before we can compare the size of a Celsius degree and a Kelvin, it’s important to understand how each scale works:
Celsius (°C)
- The Celsius scale, also known as the Centigrade scale, is based on the freezing and boiling points of water at 1 atmosphere of pressure.
- 0°C: The freezing point of water.
- 100°C: The boiling point of water (under standard atmospheric pressure).
Kelvin (K)
- The Kelvin scale is the SI (International System of Units) base unit for temperature and is used primarily in scientific contexts.
- The key difference between Kelvin and Celsius is that the Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero (0 K), which is the theoretical point where particles have minimal motion.
- 0 K: Absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature, where molecular motion stops.
- The size of a degree on the Kelvin scale is exactly the same as that of a degree on the Celsius scale, but the Kelvin scale does not have negative numbers. This means 0 K is equivalent to -273.15°C.
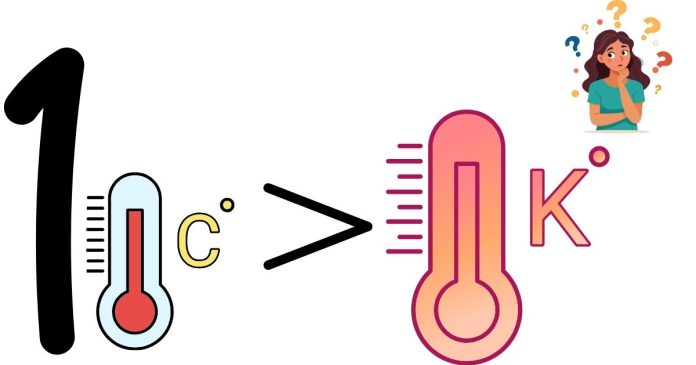
Is One Celsius Degree Larger Than a Kelvin?
No, a degree Celsius is not larger than a Kelvin; they are actually the same size! The key distinction is that they are offset by a constant value, but the size of the degree (or unit of temperature) in each scale is identical.
Why Are the Sizes of a Celsius Degree and a Kelvin the Same?
Both scales use the same increment to measure temperature changes, meaning that a change of 1°C is equivalent to a change of 1 K. This means:
- A temperature change of 1°C is the same as a temperature change of 1 K.
The Difference Lies in the Zero Points
- The difference between Celsius and Kelvin is simply their zero points:
- 0°C is the freezing point of water, while 0 K is absolute zero (the point at which molecular motion theoretically stops).
- Celsius is often used for everyday temperature measurement, while Kelvin is primarily used in scientific applications, especially in fields like physics and chemistry.
To convert between Celsius and Kelvin, you simply add or subtract 273.15:
- Kelvin = Celsius + 273.15
- Celsius = Kelvin – 273.15
Practical Example
If you have a temperature of 25°C:
- To convert it to Kelvin:
25°C + 273.15 = 298.15 K
If you have a temperature of 300 K:
- To convert it to Celsius:
300 K – 273.15 = 26.85°C
Notice how the size of the temperature change remains the same, whether you’re using Celsius or Kelvin. The only difference is the zero point.
Why This Matters
While the size of a degree is the same, the use of Celsius and Kelvin varies depending on the context:
- Celsius is more suitable for everyday, practical uses (e.g., weather, cooking, etc.).
- Kelvin is used in scientific experiments and thermodynamics because it provides an absolute scale, with 0 K representing the absolute lowest possible temperature.
To answer the original question, one Celsius degree is not larger than a Kelvin. In fact, a degree on the Celsius scale is exactly the same size as a degree on the Kelvin scale. The difference between the two scales lies in their starting points: Celsius uses the freezing point of water as its zero, while Kelvin starts at absolute zero. This makes them useful for different applications, but in terms of temperature change, they are identical.