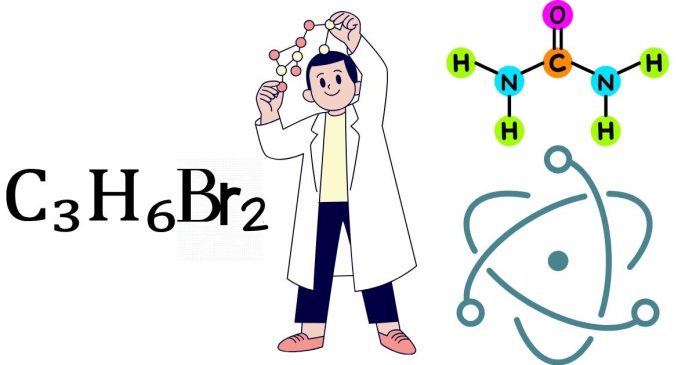
The molecular polarity of C₃H₆Br₂ (1,2-dibromopropane or 1,3-dibromopropane) depends on its structure and the distribution of electron density. In this article, we will analyze whether this compound is polar or nonpolar by considering its molecular geometry, dipole moments, and symmetry.
Step 1: Understanding the Molecular Structure
C₃H₆Br₂, or dibromopropane, is a three-carbon hydrocarbon chain (propane) with two bromine (Br) atoms attached at different positions. There are two main structural isomers:
- 1,2-Dibromopropane – Bromine atoms are attached to the first and second carbon.
- 1,3-Dibromopropane – Bromine atoms are attached to the first and third carbon.
Each structure has different symmetry, affecting its polarity.
Step 2: Electronegativity and Dipole Moments
- Bromine (Br) is highly electronegative (about 2.96 on the Pauling scale), meaning it attracts electrons more than carbon (2.55) and hydrogen (2.20).
- This creates polar covalent bonds (C–Br), where the electron density is pulled toward bromine.
- Polarity depends on whether these dipoles cancel out or create an overall dipole moment in the molecule.
Step 3: Determining Molecular Polarity
1,2-Dibromopropane: Polar
- The two bromine atoms are positioned asymmetrically on adjacent carbon atoms.
- This creates an uneven electron distribution across the molecule.
- Since the dipole moments from each C–Br bond do not cancel out, 1,2-dibromopropane is polar.
1,3-Dibromopropane: Nonpolar
- The bromine atoms are placed symmetrically at opposite ends of the propane chain.
- This symmetry causes the dipole moments to cancel out, leaving no net dipole.
- As a result, 1,3-dibromopropane is nonpolar.
Is C₃H₆Br₂ Polar or Nonpolar?
- 1,2-Dibromopropane is polar because its dipole moments do not cancel out.
- 1,3-Dibromopropane is nonpolar because of its symmetrical structure.
Thus, the polarity of C₃H₆Br₂ depends on which structural isomer you are referring to!