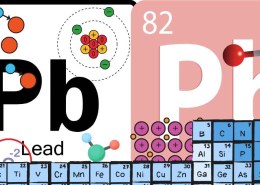
Lead () is an element that can form ions with different charges, depending on how many electrons it loses. The most common ionic charges of lead are:
1. +2 Charge (): This happens when lead loses two of its outer electrons. This form is known as the Lead(II) ion or plumbous ion, and it is the most stable and commonly found form of lead in compounds like lead(II) oxide (PbO).
2. +4 Charge (): In this case, lead loses four electrons, forming the Lead(IV) ion or plumbic ion. It is less stable than the +2 charge but occurs in compounds like lead(IV) oxide (PbO₂).
The ability of lead to form these two charges comes from its position in the periodic table as a post-transition metal, where it can use its outermost electrons (in the and orbitals) to form ions.