In a human arm, the phalanges are distal to the carpals (the wrist bones) and proximal to the phalanges of the fingers (meaning they are part of the same structure). Here’s a more detailed explanation:
- Distal: The phalanges are distal to the carpals, meaning they are farther away from the point of attachment (the shoulder or trunk of the body).
- Proximal: The phalanges of the hand (fingers) are proximal to the tips of the fingers, as they are closer to the body.
So, to fill in the blank:
“In a human arm, the phalanges are distal to the carpals.”
Let’s break down the details:
1. Anatomical Terms of Direction
In human anatomy, terms like distal, proximal, superior, inferior, medial, and lateral are used to describe the position of body parts relative to each other. Here’s how distal and proximal are used:
- Distal: Refers to a point farther from the center of the body or the origin of a limb. In other words, it’s used to describe parts that are located further away from the trunk or torso.
- Proximal: Refers to a point closer to the center of the body or the origin of a limb.
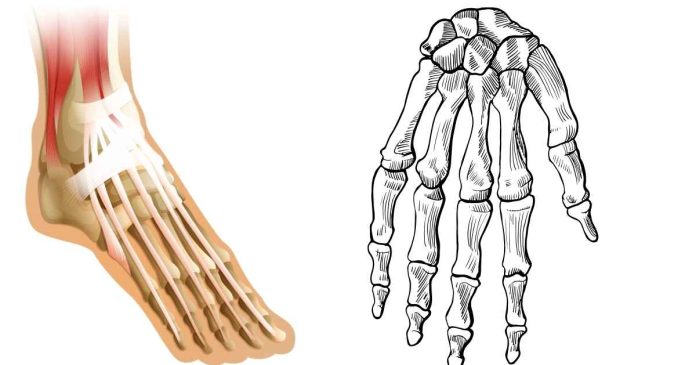
2. The Phalanges in the Human Arm
The human hand consists of several bones:
- Phalanges: These are the bones of the fingers and toes. In the hand, each finger (except the thumb) has three phalanges: the proximal phalanx (closer to the palm), the middle phalanx (between the proximal and distal phalanges), and the distal phalanx (the tip of the finger).
- Carpals: These are the eight bones that make up the wrist.
3. Describing the Relationship of the Phalanges and Carpals
- The phalanges are distal to the carpals: The phalanges are farther from the center of the body (since they make up the fingers) compared to the carpals, which are closer to the body (they are located in the wrist). So, the phalanges are distal to the carpals.
- The phalanges are proximal to the fingertips: The phalanges are closer to the body when considering the structure of the hand, as the fingertips are at the farthest end of the fingers.
4. Detailed Example:
- If we are talking about a specific finger:
- The proximal phalanx is the bone closest to the palm of your hand.
- The distal phalanx is the bone at the tip of your finger, farthest from the hand.
So, if we describe the relationship between the phalanges and the carpals, we would say that the phalanges are distal to the carpals because they are further from the center of the body and toward the tip of the fingers. Similarly, the carpals are proximal to the phalanges because they are closer to the body.
5. Other Examples of Distal and Proximal in the Upper Limb:
- Upper arm (humerus) is proximal to the forearm bones (radius and ulna).
- Forearm (radius and ulna) is proximal to the carpals.
- Carpals are proximal to the phalanges (as already explained).
Summary
So, the full statement would be:
- “In a human arm, the phalanges are distal to the carpals.” This means the phalanges (bones of the fingers) are located farther from the center of the body than the carpals (bones of the wrist).