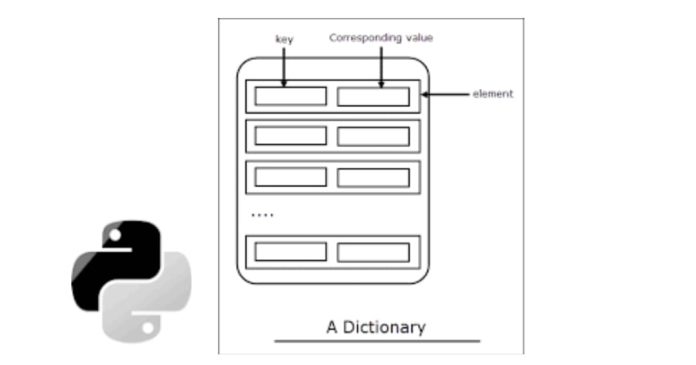
In Python, dictionaries can be sorted by key or value using built-in functions like sorted().
Sort by Key:
To sort a dictionary by key, use sorted() with the key parameter, which sorts the keys in ascending order by default.
Example:
python
my_dict = {‘b’: 3, ‘a’: 1, ‘c’: 2}
sorted_dict = {k: my_dict[k] for k in sorted(my_dict)}
print(sorted_dict) # Output: {‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 3, ‘c’: 2}
Sort by Value:
To sort a dictionary by value, use sorted() and specify a key function that sorts based on dictionary values.
Example:
python
my_dict = {‘b’: 3, ‘a’: 1, ‘c’: 2}
sorted_by_value = {k: v for k, v in sorted(my_dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[1])}
print(sorted_by_value) # Output: {‘a’: 1, ‘c’: 2, ‘b’: 3}
Descending Order:
For descending order, add the reverse=True argument in sorted().
Sorting dictionaries allows for better data organization and retrieval based on keys or values