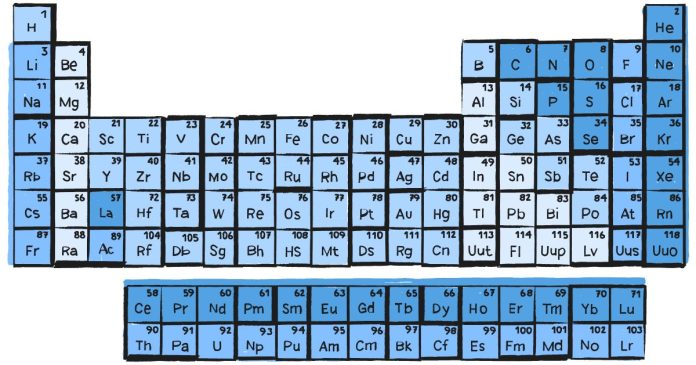
Where Are the Non-Metals Located in the Periodic Table?
The periodic table is a systematic arrangement of elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. Among these elements, non-metals are a group distinguished by their lack of metallic characteristics, such as conductivity, malleability, and luster. These elements play crucial roles in both chemistry and biology. Understanding their position on the periodic table is key to understanding their behavior.
Location of Non-Metals in the Periodic Table
Non-metals are primarily located on the right side of the periodic table, with a few exceptions. They are positioned in groups and regions that distinguish them from metals and metalloids. Here’s a closer look:
1. Upper Right Corner
- The majority of non-metals are found in the upper right corner of the periodic table.
- This region includes elements from Groups 14 (IVA) to 18 (VIIIA), excluding the metalloids that appear in the same groups.
2. Hydrogen
- Hydrogen is an exception among non-metals because it is located in Group 1 (IA), above the alkali metals.
- Despite its position, hydrogen is a non-metal due to its unique properties and is often considered separately from other groups.
Groups Containing Non-Metals
The following groups include non-metal elements:
Group 14 (Carbon Group)
- Carbon (C) is the only non-metal in this group. It forms the backbone of organic compounds and is essential to life.
Group 15 (Nitrogen Group)
- Includes Nitrogen (N) and Phosphorus (P) as non-metals. These elements are vital for biological molecules like DNA and proteins.
Group 16 (Oxygen Group or Chalcogens)
- Includes Oxygen (O), Sulfur (S), and Selenium (Se) as non-metals. These elements play roles in respiration, minerals, and more.
Group 17 (Halogens)
- Comprises Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I), and Astatine (At), known for their reactivity and role in forming salts.
Group 18 (Noble Gases)
- Includes Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe), and Radon (Rn). These are inert, non-reactive gases under standard conditions.
Key Properties of Non-Metals
- Physical Properties: Non-metals are generally brittle when solid, lack metallic luster, and are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- Chemical Properties: They tend to gain or share electrons during chemical reactions, making them good oxidizing agents.
- States of Matter: Non-metals exist in all three states at room temperature—gases (e.g., oxygen), liquids (e.g., bromine), and solids (e.g., sulfur).
Comparison with Other Element Groups
- Metalloids: Non-metals are adjacent to metalloids, which share properties of both metals and non-metals.
- Metals: Found predominantly on the left and center of the periodic table, metals differ significantly in their conductivity, malleability, and chemical behavior.