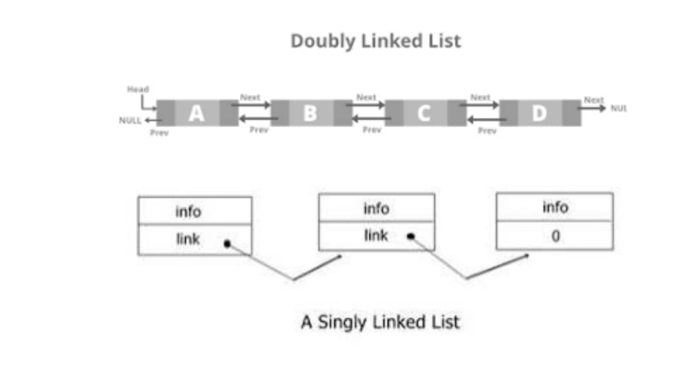
Creating a linked list in C involves defining a structure for the nodes and implementing functions to manipulate the list, such as insertion, deletion, and traversal.
A linked list consists of nodes, where each node contains data and a pointer to the next node.
Steps to Create a Linked List:
1. Define the Node Structure:
Each node holds data and a pointer to the next node.
c
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
2. Create a New Node:
Allocate memory for a new node and initialize it.
c
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
3. Insert at the Beginning:
Insert a new node at the start of the list.
c
void insertAtBeginning(struct Node** head, int data) {
struct Node* node = newNode(data);
node->next = *head;
*head = node;
}
4. Traverse and Print the List:
c
void printList(struct Node* head) {
while (head != NULL) {
printf(“%d -> “, head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf(“NULL\n”);
}
Example Usage:
c
int main() {
struct Node* head = NULL;
insertAtBeginning(&head, 10);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 20);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
This will create a simple linked list and print its contents.