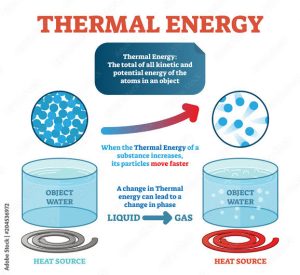
The thermal energy of an object, also known as its internal energy, is defined as the total energy of the object due to the motion of its particles. It is a measure of the kinetic energy of the particles that make up the object, and it is directly related to the object’s temperature.
 Source: Google
Source: Google
In other words, thermal energy is the energy that an object possesses due to the random motion of its atoms or molecules. As the temperature of an object increases, the particles that make up the object gain kinetic energy and start moving faster, resulting in an increase in the object’s thermal energy.
Thermal energy is typically measured in units of joules (J) and is a function of the object’s mass, specific heat capacity, and temperature. It can be calculated using the formula:
Thermal Energy (Q) = mcΔT
Where:
m = mass of the object
c = specific heat capacity of the object
ΔT = change in temperature
Thermal energy is an important concept in thermodynamics and is used to describe the behavior of objects and systems in terms of their energy interactions.


