How Are the Frequency and Wavelength of Light Related?
Understanding the relationship between frequency and wavelength is key to grasping the nature of light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation. Here’s a comprehensive look at how these two fundamental properties are interconnected.
Frequency of Light
- Definition: Frequency refers to the number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time. In the context of light, it represents how often the wave oscillates as it travels through space.
- Unit: Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz), where one hertz equals one cycle per second.
- Higher Frequency: High-frequency light waves have more wave cycles per second, corresponding to shorter wavelengths.
- Lower Frequency: Conversely, low-frequency light waves have fewer wave cycles per second, corresponding to longer wavelengths.
Wavelength of Light
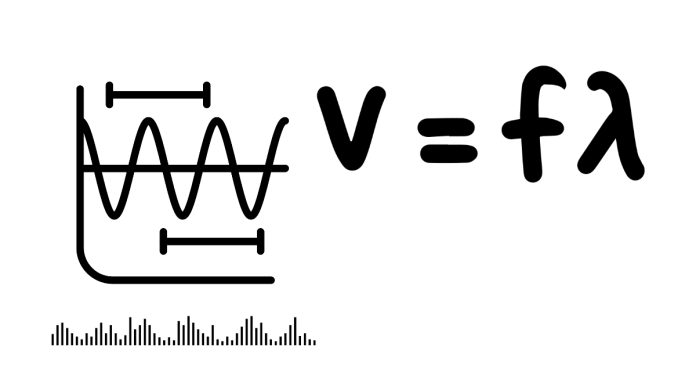
- Definition: Wavelength is the distance between two successive crests (or troughs) of a wave, representing the physical length of one wave cycle.
- Unit: Wavelength is typically measured in meters (m) or nanometers (nm) for light waves.
- Shorter Wavelengths: Light waves with shorter wavelengths have higher frequencies.
- Longer Wavelengths: Light waves with longer wavelengths have lower frequencies.
Inverse Relationship
- Mathematical Relationship: The frequency ff of light and its wavelength λ\lambda are inversely proportional to each other. f=cλf = \frac{c}{\lambda} Where:
- ff is the frequency of light in hertz (Hz).
- cc is the speed of light in a vacuum (~3.00 x 10^8 meters per second).
- λ\lambda (lambda) is the wavelength of light in meters.
Practical Implications
- Color Perception: Different wavelengths of light correspond to different colors in the visible spectrum, from violet (short wavelength, high frequency) to red (long wavelength, low frequency).
- Applications: Understanding the relationship between frequency and wavelength is crucial in fields such as telecommunications, optics, and astronomy.
Frequency and wavelength are fundamental properties that define the characteristics of light waves. Their inverse relationship governs how light behaves and is perceived across various applications and scientific disciplines.
By comprehending this relationship, we gain deeper insights into the nature of light and its myriad applications in our modern world.
Let me know if you need any further adjustments or additions!