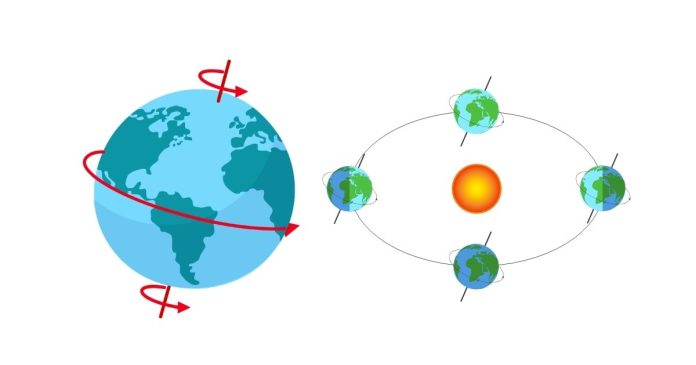
The terms rotation and revolution describe motion, but they refer to distinct types of movement. Here’s an explanation of the differences:
1. Rotation
- Definition: Rotation is the spinning of an object around its axis.
- Example: The Earth rotates around its axis, which causes day and night.
- Key Features:
- It happens internally, meaning the axis of rotation passes through the object itself.
- For Earth, one full rotation takes approximately 24 hours.
- Rotation direction can be described as clockwise or counterclockwise when viewed from a specific perspective.
- Real-Life Examples:
- A spinning top rotates around its center.
- The wheels of a car rotate as it moves.
2. Revolution
- Definition: Revolution is the movement of one object around another object.
- Example: The Earth revolves around the Sun, which causes the seasons.
- Key Features:
- It happens externally, meaning the object moves around a point or another body.
- For Earth, one complete revolution around the Sun takes approximately 365.25 days.
- The path of revolution is usually an elliptical orbit.
- Real-Life Examples:
- The Moon revolves around the Earth.
- Planets in the solar system revolve around the Sun.
Key Differences
| Feature | Rotation | Revolution |
|---|---|---|
| Motion Type | Spins on its axis | Orbits around another object |
| Examples | Earth’s day and night cycle | Earth’s yearly cycle around the Sun |
| Timeframe (Earth) | ~24 hours | ~365.25 days |
| Axis/Center | The internal axis passes through it | External focus, such as the Sun |
Summary
- Rotation is like spinning in place, while revolution is like traveling in a circle around something else.
- Both motions are crucial in celestial mechanics, influencing phenomena like seasons, day-night cycles, and tidal forces.