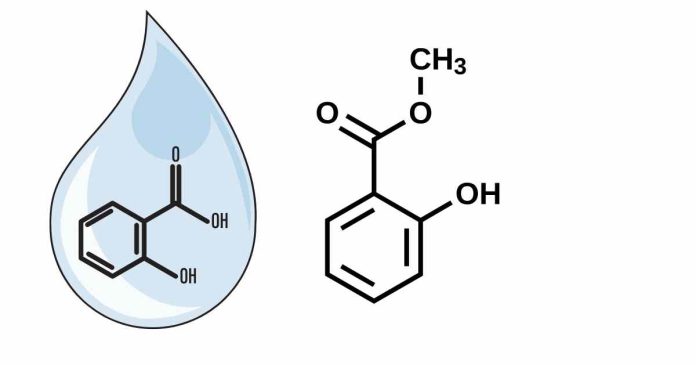
Equation for the Saponification of Methyl Salicylate?
The reaction produces sodium salicylate and methanol:
C8H8O3 + NaOH -> C7H5O3Na + CH3OH
Here’s a more detailed explanation of the saponification reaction of methyl salicylate:
Reaction Equation
C₈H₈O₃ (methyl salicylate) + NaOH (sodium hydroxide) → C₇H₆O₃Na (sodium salicylate) + CH₃OH (methanol)
Reaction Type
Saponification reaction (hydrolysis of an ester)
Reaction Conditions
– Typically performed in aqueous solution
– Requires a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
– Often carried out at elevated temperatures (around 50-100°C)
Mechanism
1. Nucleophilic attack: The hydroxide ion (OH⁻) from sodium hydroxide attacks the carbonyl carbon of methyl salicylate.
2. Formation of a tetrahedral intermediate: The hydroxide ion forms a bond with the carbonyl carbon, creating a tetrahedral intermediate.
3. Breakdown of the intermediate: The intermediate breaks down, forming sodium salicylate and methanol.
Importance
The saponification reaction of methyl salicylate is significant in the production of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), as it allows for the conversion of methyl salicylate to sodium salicylate, which can then be further reacted to form aspirin.