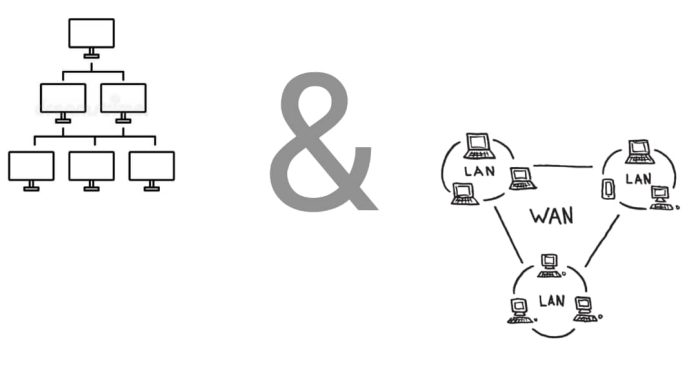
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that spans a small geographical area, such as a home, office, or building. It is typically characterized by high data transfer speeds, low latency, and relatively low cost. LANs often use wired connections (Ethernet) or wireless technologies (Wi-Fi) to connect devices such as computers, printers, and servers within close proximity.
A Wide Area Network (WAN), on the other hand, covers a large geographical area, potentially spanning cities, countries, or even continents. WANs connect multiple LANs and other networks, often relying on leased telecommunications lines or public infrastructure like the internet. While WANs provide global connectivity, they tend to have higher latency, slower speeds, and greater setup and maintenance costs compared to LANs.
In summary, LANs are for local, high-speed connections, while WANs are designed for long-distance communication, connecting multiple LANs over large areas.