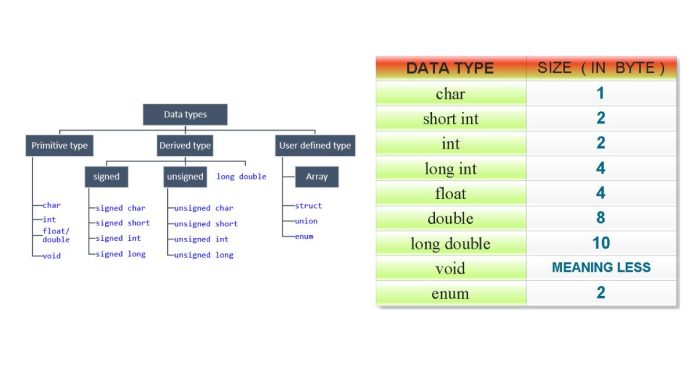
Data types in C define the type of data that a variable can hold. They determine the size and type of memory that a variable occupies and the operations that can be performed on it.
1. Basic Data Types
These are the fundamental data types provided by the C language.
| Data Type | Size (in bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|
int |
2 or 4 | Stores integers (whole numbers). |
float |
4 | Stores single-precision floating-point numbers. |
double |
8 | Stores double-precision floating-point numbers. |
char |
1 | Stores a single character. |
_Bool |
1 | Stores Boolean values (true or false). |
2. Derived Data Types
These are constructed from basic data types.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Array | Collection of elements of the same data type. |
| Pointer | Stores the address of another variable. |
| Structure | Combines variables of different data types. |
| Union | Combines variables of different types sharing memory. |
| Function | A block of code that performs a specific task. |
3. Enumerated Data Type
- Defined using the
enumkeyword. - Used to assign names to integral constants for better readability.
Example:
4. Void Data Type
- Represents the absence of any value.
- Commonly used for functions that do not return a value.
Example:
Modifiers for Basic Data Types
Modifiers alter the size and range of basic data types.
| Modifier | Used With | Description |
|---|---|---|
signed |
int, char |
Allows storage of both positive and negative values. |
unsigned |
int, char |
Stores only positive values. |
short |
int |
Reduces the size of an integer. |
long |
int, double |
Increases the size of the data type. |
Ranges of Common Data Types
| Data Type | Range |
|---|---|
char |
-128 to 127 (signed) |
unsigned char |
0 to 255 |
int |
-32,768 to 32,767 (16-bit) |
unsigned int |
0 to 65,535 (16-bit) |
float |
3.4E-38 to 3.4E+38 |
double |
1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308 |
Examples of Variable Declarations
Why Data Types Are Important
- Memory Efficiency: Helps allocate the right amount of memory.
- Type Safety: Ensures correct operations on variables.
- Performance: Optimizes code execution by using appropriate types.
Understanding data types in C is fundamental to writing efficient and error-free programs.