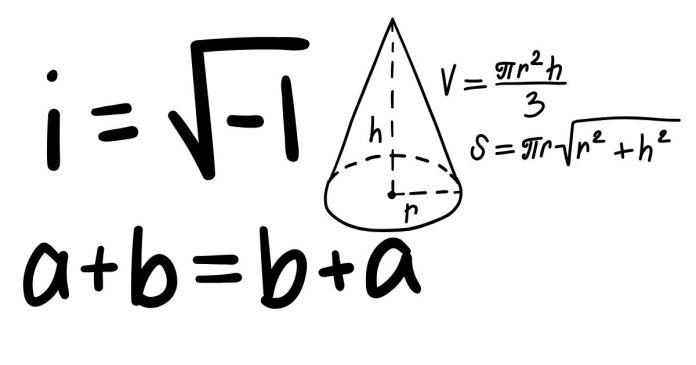Cone: Definition, Formula, Types, Examples, and Properties
Definition:
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that has a flat, circular base and a single vertex (apex) that is not in the plane of the base. The surface of the cone is formed by all line segments that connect the vertex to the points of the boundary of the base. A cone can be thought of as a pyramid with a circular base.
Formulae:
For a cone, there are a few key formulas to know:
- Surface Area (SA): The total surface area of a cone includes both the area of the base and the lateral surface area (the side surface).
SA=πr2+πrlSA = \pi r^2 + \pi r lWhere:
- rr = radius of the base
- ll = slant height of the cone
- π\pi = 3.1416 (constant)
- Volume (V): The volume of a cone is given by the formula:
V=13πr2hV = \frac{1}{3} \pi r^2 hWhere:
- rr = radius of the base
- hh = height of the cone (distance from the base to the apex)
Types of Cones:
- Right Cone:
- In a right cone, the apex is directly above the center of the base. The axis (line joining the apex to the center of the base) is perpendicular to the base.
- The slant height and height are distinct.
- Oblique Cone:
- In an oblique cone, the apex is not directly above the center of the base. The axis is tilted, meaning the cone is “slanted” or “tilted” relative to the base.
- The slant height is different from the height in this case.
Examples:
- Ice Cream Cone:
- A classic example of a cone is an ice cream cone, where the base is circular and the cone narrows to a point at the top.
- Traffic Cones:
- Cones used in roadways and parking lots are typically shaped like a truncated cone (a cone with the top cut off).
Properties of a Cone:
- Base: A cone always has a circular base.
- Height: The height is the perpendicular distance from the apex to the center of the base.
- Slant Height: The slant height is the distance between the apex and any point on the circumference of the base along the side of the cone.
- Volume: The volume of a cone is one-third of the volume of a cylinder with the same base and height.
- Surface Area: The surface area of a cone includes both the lateral surface and the base area.
- Symmetry: A cone has rotational symmetry around its axis.
Conclusion:
A cone is a well-known geometric shape that has various real-world applications, from architectural structures to everyday objects. Its properties, such as surface area and volume, are essential in understanding how the shape behaves in space, and the formulas provided help in computing various characteristics of a cone efficiently.