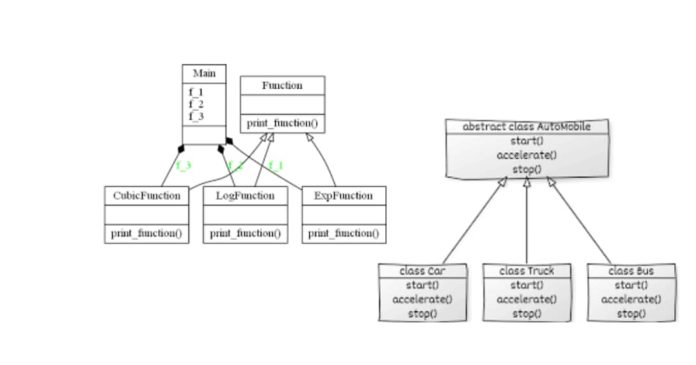
In Python, abstract classes are classes that cannot be instantiated directly and are meant to be subclassed. They serve as blueprints for other classes, defining methods that must be implemented in any concrete (non-abstract) subclass.
Abstract classes are defined using the abc (Abstract Base Classes) module. A class is made abstract by inheriting from ABC and using the @abstractmethod decorator for methods that must be implemented by subclasses.
Example:
python
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Animal(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def sound(self):
pass
class Dog(Animal):
def sound(self):
return “Bark”
# animal = Animal() # This will raise an error
dog = Dog()
print(dog.sound()) # Output: Bark
Key Points:
– Abstract classes cannot be instantiated.
– They can have abstract methods and concrete methods.
– Subclasses must implement all abstract methods to be instantiated.
Abstract classes help enforce a consistent interface across multiple subclasses.